Understanding Calories: The Basics
Calories are a unit of measurement used to quantify the amount of energy provided by food and beverages consumed. In the context of nutrition, they serve as a crucial indicator of how much energy one gains through food intake and subsequently expends through daily activities. The balance between calories consumed and calories burned is essential for maintaining body weight and overall health.
When we consume food, our bodies metabolize these items to release energy in the form of calories. This energy is utilized by the body to support various physiological functions, ranging from basic mechanisms like breathing and circulation to voluntary actions such as exercising and engaging in daily tasks. In essence, calories are fundamental to providing the fuel needed for life processes.
In addition to understanding the intake of calories, it is vital to recognize how they are “burned.” Physical activity plays a significant role in this regard. Activities such as walking, running, cycling, and even less vigorous forms of exercise contribute to the total energy expenditure. Additionally, the process of digestion and metabolism itself requires energy, which presents another avenue for calories to be burned, even when at rest.
Another important concept in calorie understanding is the Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), which refers to the number of calories the body requires to maintain basic physiological functions while at rest. BMR accounts for a significant portion of an individual’s overall calorie needs and is influenced by factors such as age, gender, weight, and muscle mass. Knowing one’s BMR can aid in determining daily calorie requirements for maintaining, losing, or gaining weight, thereby supporting an individual’s overall goal for a healthy lifestyle.
How to Calculate Your Daily Caloric Needs
Understanding how to calculate your daily caloric needs is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Caloric needs vary depending on several factors, such as age, weight, height, gender, and activity level. The most commonly used method to estimate daily caloric requirements is the Mifflin-St Jeor equation, which has separate formulas for men and women. For men, the equation is: Calories = 10 x weight (kg) + 6.25 x height (cm) – 5 x age (years) + 5. For women, the formula is similar, but it concludes with -161 instead of +5.
In addition to age, weight, height, and gender, the level of physical activity plays a significant role in determining daily caloric needs. To account for activity level, you can multiply your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)—calculated using the aforementioned equations—by an activity factor. The general categories are sedentary (BMR x 1.2), lightly active (BMR x 1.375), moderately active (BMR x 1.55), very active (BMR x 1.725), and extra active (BMR x 1.9). This step helps provide a more tailored caloric estimate.
There are also online calculators and apps that can assist in determining caloric needs, often presenting results based on both the Mifflin-St Jeor equation and activity levels. To visualize this process, incorporating infographics or instructional videos can enhance understanding. These resources can effectively illustrate not only the calculation methods but also how different factors influence caloric needs.
By accurately calculating your daily caloric needs, you can better strategize your dietary intake and exercise regime, ultimately contributing to a healthier lifestyle. Adopting a data-driven approach can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their nutrition and fitness goals.

Balancing Calories for Weight Management
Achieving a calorie balance is a pivotal aspect of effective weight management, whether the goal is weight loss, maintenance, or gain. Understanding this balance involves aligning caloric intake with expenditure, which can be mastered through a combination of informed dietary choices and regular exercise. To foster sustainability in one’s lifestyle, it is vital to prioritize gradual changes rather than resorting to extreme dieting, which may lead to adverse effects on overall health and well-being.
When aiming for weight loss, creating a calorie deficit by consuming fewer calories than the body uses is essential. However, this does not necessitate severely limiting food intake. Instead, individuals can focus on nutrient-dense foods that are lower in calories yet high in essential vitamins and minerals. Foods such as vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains not only help individuals feel satiated but also provide necessary nutrients, contributing to a balanced diet.
For those striving to maintain their weight, it is essential to identify a caloric equilibrium. This is achieved by carefully monitoring energy intake alongside physical activity. Meal planning can be a practical approach to ensure a balanced diet, as it enables individuals to prepare healthy meals in advance, promoting portion control and reducing the likelihood of unhealthy snacking. Visual aids, such as portion control plates or food scales, can further assist in the proper distribution of food groups at meal times.
On the other hand, individuals looking to gain weight should focus on consuming a surplus of calories in a healthy manner. This might include incorporating energy-dense foods such as nuts, avocados, and whole grains into their meals. Balancing calorie intake with nutrient quality is crucial in this phase as well, ensuring that the additional calories are nourishing and supportive of overall health.
Integrating Exercise to Enhance Caloric Burn
Incorporating different forms of exercise into one’s daily routine is fundamental for enhancing caloric burn and achieving a healthy lifestyle. Exercise not only helps in increasing the metabolic rate but also plays a significant role in building muscle mass, which further aids in caloric expenditure. There are various types of exercises that one can engage in, and understanding their respective impacts on caloric burn is essential.
Cardiovascular exercises, commonly known as cardio, are among the most effective means of burning calories. Activities such as running, swimming, cycling, and brisk walking elevate the heart rate and increase oxygen consumption, resulting in significant energy expenditure. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is a particularly efficient form of cardio, characterized by short bursts of intense activity followed by rest or low-intensity periods. This approach not only burns a substantial number of calories during the workout but also promotes an elevated metabolic rate post-exercise, a phenomenon known as the afterburn effect.
Strength training complements cardio by building lean muscle mass, which inherently burns more calories at rest compared to fat tissue. Incorporating exercises such as weightlifting, resistance bands, and bodyweight exercises—push-ups, squats, and lunges—can enhance overall strength and muscle tone. Regular strength training sessions, typically conducted two to three times a week, help maintain muscle health, especially as one ages.
Moreover, integrating flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga or Pilates, can improve overall physical fitness and well-being. Although not typically associated with high caloric burn, these activities enhance body awareness and posture, contributing to a more effective exercise regimen. Utilizing video demonstrations and images can be advantageous for illustrating proper techniques, ensuring safety and effectiveness as individuals embark on their fitness journey.
The Role of Nutritional Quality in Health
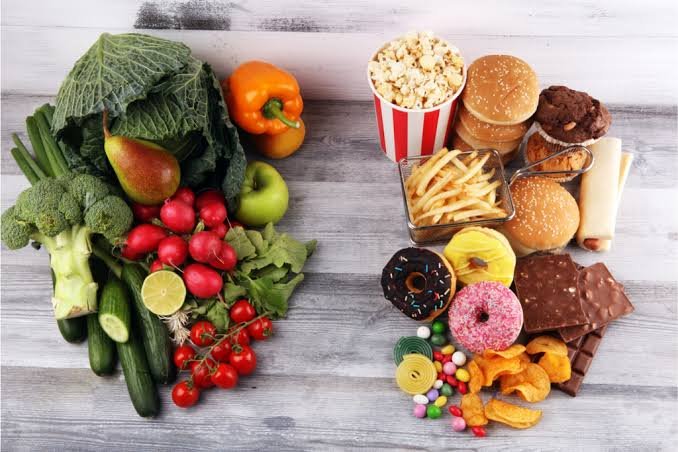
When discussing calorie intake, it is essential to consider not only the quantity but also the quality of the calories consumed. The concept of nutritional quality encompasses the spectrum of macronutrients and micronutrients present in food. Macronutrients, which include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, serve as the primary sources of energy for the body. However, the quality of these macronutrients significantly influences overall health, as whole foods tend to provide essential vitamins and minerals that processed foods often lack.
Whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, are packed with nutrients that contribute to various bodily functions, including immune response, digestion, and cognitive health. For instance, colorful fruits and vegetables contain antioxidants and phytonutrients that can reduce inflammation and enhance wellness. In contrast, processed foods, which are often high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, offer little in terms of nutritional benefits and can lead to a host of health issues, such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
Furthermore, the consumption of high-quality calories from whole foods promotes satiety and aids in weight management. When individuals prioritize nutritional quality over merely counting calories, they are more likely to feel satisfied and energized, which can ultimately lead to healthier eating patterns. Emphasizing the importance of meal preparation with whole food ingredients can inspire readers to make conscious dietary choices, thus fostering a sustainable approach to nutrition.
Incorporating a variety of colorful, nutrient-dense foods into the diet can transform meals into health-enhancing experiences. Therefore, understanding the role of nutritional quality is paramount for anyone aiming for a healthy lifestyle, as it lays the foundation for achieving optimal health and well-being.
Tracking Your Caloric Intake: Tools and Techniques
In the pursuit of a healthy lifestyle, tracking caloric intake is essential for maintaining a balanced diet. Fortunately, a variety of tools and applications are available to help streamline this process. One of the most popular methods is using mobile apps designed specifically for tracking meals and calories. MyFitnessPal, Lose It!, and Cronometer are among the leading choices, each offering unique features that cater to different user preferences.
To use these apps effectively, it is vital to understand how to log your meals accurately. Begin by recording each item you consume, paying close attention to portion sizes. Most applications allow users to search for specific foods in their databases, making it easy to find entries that detail caloric content and nutritional information. For items not readily available in the app, you can manually enter the nutritional values listed on packaging.
Reading nutrition labels is a fundamental skill that complements calorie tracking. Familiarizing yourself with the various components of these labels, including serving sizes, calories, and macronutrients, aids in making informed dietary choices. Remember that the serving size indicated may not always align with your consumption. Thus, adjust your entries in the app accordingly to ensure accurate tracking.
Another efficient technique involves the use of barcode scanning, which many calorie-tracking apps support. This feature allows users to simply scan the barcode of a food product, instantly providing the associated nutritional information. Utilizing this tool can significantly reduce the time spent logging meals and increase accuracy, as the app often fills in details automatically.
Incorporating these tools and techniques into your daily routine can greatly simplify the process of monitoring caloric intake, ultimately contributing to healthier eating habits and lifestyle choices.
Common Mistakes in Calorie Calculation
Calorie counting can be a crucial component of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, yet many individuals fall prey to common miscalculations that can undermine their efforts. One of the most prevalent mistakes is underestimating portion sizes. It is easy to overlook the fact that serving sizes can vary significantly from the ideal portions outlined on nutritional labels. For instance, a single serving of pasta is often quantified as just one cup, yet many people consume upwards of two or three cups in a single meal. This misjudgment can lead to an inadvertent spike in calorie intake, which can disrupt weight management goals.
Another frequently encountered issue is neglecting to account for snacks. Many individuals may meticulously log their meals yet dismiss the small calorie intake from snacks throughout the day. This oversight can lead to a significant miscalculation of total daily calories and may contribute to unwanted weight gain. For example, a few handfuls of nuts or a couple of chocolate bars may seem inconsequential in the moment but can aggregate into a considerable amount of calories over the course of a week.
Additionally, many people mistakenly believe that all calorie values provided by apps and calculators are completely accurate. While these tools can be beneficial, they may also rely on generalized data that does not account for individual metabolic rates or unique nutritional needs. Therefore, it is essential to approach any calorie calculation with a critical mindset, considering personal factors such as age, gender, activity level, and overall health. By recognizing these common pitfalls, individuals can enhance their calorie management efforts and make more informed dietary choices.
Staying Motivated: Tips for Long-Term Success
Maintaining motivation in a healthy lifestyle, particularly when it comes to calorie management and exercise, can present challenges. However, adopting effective strategies can significantly enhance an individual’s commitment to long-term health goals. Setting achievable goals is foundational. Start with specific, measurable objectives that can be accomplished in a realistic timeframe. For instance, aiming to lose a certain number of pounds in a month, or walking a specified number of steps daily are manageable targets that encourage consistent effort. It is essential that these goals progress over time to prevent stagnation.
Another vital strategy involves finding a support network. Engaging with support groups can provide emotional encouragement and accountability, making the journey toward a healthy lifestyle more enjoyable. Whether through online forums, local meet-ups, or fitness classes, connecting with like-minded individuals can foster an environment of shared commitment and motivation. Additionally, regularly participating in group activities can enhance feelings of morale and boost engagement in calorie management and exercise routines.
Incorporating rewards for achieving milestones is another effective motivational technique. Rewarding oneself for reaching specific goals—such as treating oneself to a small gift or a relaxing day off—can serve as a positive reinforcement, encouraging continued dedication to a healthy lifestyle. It is imperative that these rewards align with the overall objective of health improvement, steering clear of indulgences that counteract progress.
Finally, utilizing success stories in the form of videos or testimonials can inspire individuals to stay committed to their health journeys. By witnessing the transformation of others who have successfully managed their calories and embraced an active lifestyle, one may find renewed motivation and the mindset needed to keep moving toward their personal goals.
Conclusion: Putting It All Together
In summary, mastering calorie calculation is a critical component of achieving a healthy lifestyle. By understanding the relationship between calorie intake and expenditure, individuals can make informed decisions that promote overall well-being. This blog post has highlighted the essential steps involved in calculating caloric needs, emphasizing the importance of tailoring those needs to one’s unique lifestyle, goals, and activity levels.
Healthy eating plays a pivotal role in this balance. By incorporating nutrient-dense foods that align with personal energy requirements, individuals can enhance their health while effectively managing body weight. It is crucial to not only focus on the quantity of calories consumed but also on the quality of those calories. Prioritizing whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can significantly improve nutrient intake and overall health outcomes.
Moreover, regular physical activity complements calorie management by helping to burn calories, build muscle, and improve cardiovascular health. Engaging in a mix of aerobic exercises and strength training provides significant health benefits, including weight management, improved mood, and reduced risk of chronic diseases. Finding enjoyable forms of exercise can encourage consistency, making it easier to integrate physical activity into daily routines.
As you embark on your journey towards mastering calorie calculation, remember that small, sustainable changes can lead to lasting results. Begin by assessing your current eating habits and activity levels, then apply the principles discussed to create a more balanced approach. We encourage you to explore additional resources or seek professional guidance to further solidify your understanding of caloric needs and healthy habits. Embrace this journey as a lifelong commitment to health and wellness.