Strenuous activities are defined as forms of physical exertion that require significant effort, typically surpassing the average level of daily movement. These activities can involve high-intensity exercises, heavy lifting, or prolonged physical strain. Engaging in strenuous activities places considerable demands on the body’s muscles, joints, and skeletal structure, particularly impacting spinal health. Common examples of strenuous activities include weightlifting, running at an accelerated pace, participating in high-impact sports, and performing physically demanding jobs, such as construction or manual labor.
High-intensity exercises, characterized by their vigorous nature, push the body to work harder and sustain elevated heart rates. Training routines that involve plyometrics, sprinting, or circuit training fall under this category, often resulting in heightened energy expenditure and corresponding fatigue. While such exercises can offer numerous health benefits, they also pose a risk of injury, particularly to the spine. Heavy lifting, another type of strenuous activity, applies immense pressure to the spinal discs and surrounding structures. This practice, if executed incorrectly, significantly increases the likelihood of developing herniated disks, which occur when the inner gel-like substance of a spinal disc bulges out through a tear in the outer layer.
Furthermore, prolonged physical strain from engaging in strenuous activities can lead to cumulative stress on the spine. Activities that require maintaining awkward postures or repetitive motions can exacerbate existing vulnerabilities in the spinal column, potentially leading to chronic pain or injury. Understanding the impacts of strenuous activities is crucial for individuals seeking to maintain their physical health without compromising their spinal integrity. It is important to approach such activities with caution, incorporating proper technique and recovery strategies to mitigate the risks associated with intense physical exertion.
The Impact of Strenuous Activities on Herniated Disks
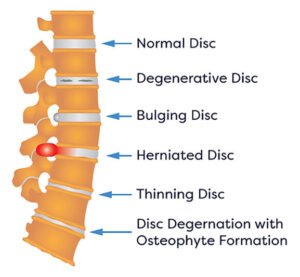
Strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting, high-intensity workouts, or repetitive physical tasks, can significantly influence the condition of herniated disks. When an individual engages in these physically demanding actions, there is a heightened risk of exacerbating existing disc herniation or creating new injuries. This section will explore the mechanisms through which strenuous activities interact with disc health, highlighting the importance of body mechanics.
One key factor in understanding the impact of strenuous activities on herniated disks is the role of excessive strain. When the spine is subjected to forces beyond its natural capacity, the intervertebral disks can become compromised. This can lead to conditions such as disc protrusion, where the jelly-like core of the disk bulges out, potentially pressing against surrounding nerves. Improper lifting techniques, such as bending at the waist instead of the knees, can amplify this risk, resulting in painful symptoms and further deterioration of the disk’s condition.
Symptoms that may arise from engaging in strenuous activities while dealing with herniated disks include persistent back pain, radiating pain into the legs, numbness, and weakness. Individuals often report an increase in discomfort following physical exertion, especially if they fail to utilize optimal body mechanics. Certain scenarios, such as participating in contact sports or high-impact aerobics, can also increase the likelihood of disk-related issues, leading to potential complications that could require medical intervention.
It is essential for individuals with herniated disks to approach strenuous activities with caution. Implementing proper techniques, utilizing supportive equipment, and allowing the body ample time for recovery can mitigate the adverse effects of strenuous exertion on disk health. Understanding this relationship is crucial for ensuring long-term spinal health and avoiding further injury.
Exercises to Avoid for Herniated Disks

Individuals with herniated disks often seek to maintain an active lifestyle; however, certain exercises and physical activities can exacerbate their condition significantly. Understanding which activities to avoid is essential for promoting recovery and preventing further injury. High-impact sports, such as basketball, football, and running, place substantial stress on the spinal column. The repetitive jarring motions common in these activities can lead to increased pressure on already compromised disks, resulting in heightened pain and discomfort.
Heavy weightlifting is another activity that should generally be avoided. Lifting heavy weights, particularly those that involve bending at the waist, can place immense strain on the lower back. Exercises such as deadlifts and squats, when performed incorrectly, can lead to further complications. Engaging in overhead lifting while lacking proper technique can also heighten the risk of exacerbating a herniated disk. Therefore, strength training should ideally focus on lighter weights with an emphasis on form, ensuring a stable spine throughout the movement.
Certain stretching techniques may inadvertently worsen the condition of individuals with herniated disks. For instance, deep forward bends and some rotational stretches can put undue stress on the vertebrae and supportive structures of the spine. It is crucial for individuals to avoid any positions that cause immediate discomfort or sharp pain, as these could indicate further injury. Instead, practicing gentle stretches that promote spinal mobility, such as pelvic tilts or gentle neck stretches, can aid in recovery.
In conclusion, recognizing exercises to avoid is vital for anyone struggling with a herniated disk. By steering clear of high-impact sports, heavy weightlifting, and potentially harmful stretching movements, individuals can take proactive steps towards their healing journey and overall well-being.
Foods to Avoid with a Herniated Disk

Maintaining a balanced diet is essential for overall spinal health, especially for individuals suffering from a herniated disk. Certain foods can exacerbate inflammation and worsen symptoms, making it crucial to be aware of potentially harmful dietary choices. The impact of diet on spinal health cannot be understated; certain foods may introduce toxins or promote inflammation, impeding the healing process and contributing to discomfort.
One significant category of foods to avoid includes highly processed items. These often contain refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and preservatives, which may contribute to systemic inflammation. For instance, sugary snacks, sodas, and commercial baked goods can elevate insulin levels, leading to increased inflammation and pain in areas affected by a herniated disk. Additionally, trans fats, commonly found in fried foods and pre-packaged snacks, can trigger inflammatory processes that could exacerbate your condition.
Another group to consider avoiding is foods rich in omega-6 fatty acids. While omega-6 is essential for the body, an excessive intake, especially in relation to omega-3 fatty acids, can result in a pro-inflammatory state. Items such as corn and soybean oils, commonly used in many fried and processed foods, should be limited. Instead, focusing on omega-3-rich alternatives like fish or flaxseeds can provide anti-inflammatory benefits.
Additionally, dairy products can also contribute to inflammation for some individuals. It is advisable to monitor your body’s response to dairy consumption and consider reducing or eliminating it if symptoms worsen. Lastly, excessive salt and processed meats have been known to lead to inflammation, further complicating herniated disk recovery. Being mindful of dietary choices will play a vital role in managing and alleviating symptoms while promoting a healthier spine.
Best Exercises for Herniated Disks
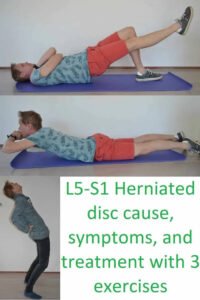


Engaging in appropriate exercise is crucial for individuals coping with herniated disks. Certain low-impact activities can provide relief, enhance stability, and promote overall spinal health without aggravating the condition. One effective exercise is gentle stretching, particularly focusing on the lower back and hamstrings. Performing stretches such as the knee-to-chest stretch helps alleviate tension in the lumbar region. To execute this stretch, lie on your back, gently pull one knee towards your chest, hold for 15-30 seconds, and then switch legs. This exercise increases flexibility and may aid in reducing discomfort.
Core strengthening exercises are also essential for individuals with herniated disks. A strong core supports the spine, thereby minimizing stress on the disks. A particularly beneficial exercise is the pelvic tilt. To perform this, lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Tighten your abdominal muscles, flattening your lower back against the floor, and hold for a few seconds before relaxing. Repeating this exercise helps improve stability and strength while being gentle on the back.
Low-impact aerobic activities, such as walking or swimming, are advantageous as they promote cardiovascular health without putting excessive strain on the spine. Swimming, in particular, is beneficial due to the buoyancy of water, which reduces stress on the back while allowing for a full range of motion. Aim for 20-30 minutes of these activities several times a week, adjusting intensity based on individual tolerance levels. It is essential to listen to your body and modify any movements that cause pain.
Engaging in these exercises consistently can lead to improved spinal health while mitigating the challenges associated with herniated disks. Always consult a healthcare professional before beginning any exercise regimen to ensure it aligns with individual health needs and conditions.
Best Foods to Incorporate for Herniated Disks


Maintaining a nutritious diet is vital for individuals dealing with herniated disks. Certain foods can provide essential nutrients that support spinal health and may alleviate associated symptoms. An emphasis on anti-inflammatory foods is crucial, as inflammation can exacerbate pain and discomfort linked to herniated disks.
One of the most beneficial groups of foods includes fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce inflammation around the spinal discs. Incorporating these fish into one’s diet at least twice a week can significantly contribute to overall spinal health.
Leafy green vegetables, including spinach and kale, are also recommended due to their high content of antioxidants and vitamins. These nutrients play a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress, which can aggravate the symptoms of herniated disks. Collard greens and broccoli are excellent choices that provide an abundance of vitamin K and calcium as well.
Other foods that promote spinal health include berries, such as blueberries and strawberries, which are packed with antioxidants and have been shown to combat inflammation. Nuts and seeds, particularly walnuts and chia seeds, are also rich in omega-3 fatty acids and can be easily added to smoothies or salads for a nutritious boost.
Additionally, it is prudent to incorporate foods high in fiber, such as whole grains, into the diet. Fiber assists in maintaining a healthy weight, which is essential for minimizing pressure on the spine. Foods like quinoa, brown rice, and oats contribute not only fiber but also important vitamins and minerals that support a healthy body overall.
In conclusion, adopting a diet rich in anti-inflammatory and nutrient-dense foods can have a positive impact on those suffering from herniated disks. By prioritizing the right foods, individuals may find relief from symptoms and support their spinal health effectively.
Sex Life Considerations for Those with Herniated Disks
A herniated disk can significantly affect various aspects of life, including intimate relationships and sexual experiences. The physical limitations imposed by pain and reduced mobility can create emotional challenges for both partners. These hurdles may lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, or inadequacy, making open communication essential in navigating the complexities of intimacy in the context of a herniated disk.
Individuals suffering from a herniated disk often experience discomfort during movement, which can lead to hesitation or avoidance of sexual activity. It is crucial for both partners to have frank discussions about how the condition affects their intimate life. This dialogue not only fosters empathy and understanding but also helps in identifying specific concerns or fears related to engaging in sexual activities. Acknowledging these sentiments can alleviate some emotional burdens while reinforcing the emotional bond between partners.
Adapting sexual activities to accommodate comfort levels can lead to a rewarding and fulfilling intimate life, despite the limitations posed by a herniated disk. Position adjustments can play a significant role in ensuring comfort for individuals experiencing pain. For instance, using pillows for support or trying different positions that minimize stress on the back can enhance the overall experience. Engaging in more gentle forms of touch or intimacy can also foster connection without exacerbating pain.
Furthermore, exploring non-penetrative sexual expressions, such as cuddling, kissing, or mutual massage, can provide a means of maintaining intimacy while prioritizing comfort. Emphasizing emotional closeness and physical affection can help preserve the quality of the relationship, even if sexual activity might look different than it did before. In conclusion, with careful communication and thoughtful adaptations, couples can maintain a satisfying sexual relationship despite the challenges posed by a herniated disk.
Understanding Sciatica and Foot Drop Related to Herniated Disks
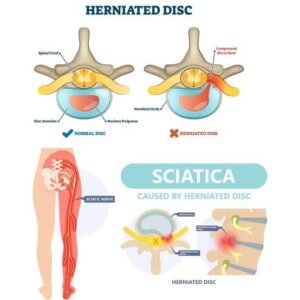


A herniated disk occurs when the soft inner material of the spinal disk protrudes through a tear in the tougher exterior. This condition can significantly impact nearby nerves, leading to a range of symptoms, including sciatica. Sciatica is characterized by pain radiating along the path of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back through the hips and buttocks and down each leg. The pain may manifest as a sharp ache, burning sensation, or even numbness, and is often provoked by certain movements or prolonged sitting. Herniated disks are a common cause of sciatica, leading to inflammation and irritation of the sciatic nerve.
Foot drop, on the other hand, is a neurological condition that results in difficulty lifting the front part of the foot. This condition may occur due to neurological or muscular disorders, but it can also be a complication from a herniated disk affecting specific nerves in the lower back. Patients may find themselves dragging their foot while walking or have an increased tendency to trip, which can compromise mobility and safety. The relationship between herniated disks, sciatica, and foot drop highlights the intricate connections within the nervous system.
Management strategies for these interlinked conditions typically focus on alleviating pain and restoring functionality. Physical therapy often plays a critical role, utilizing targeted exercises to strengthen the lower back and leg muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance coordination. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and manage pain. For individuals experiencing severe symptoms or limited relief from conservative treatments, surgical options could be explored to relieve nerve pressure. Understanding the implications of herniated disks on conditions like sciatica and foot drop is vital for effective management and rehabilitation.
Conclusion
In summary, the management of herniated disks is greatly influenced by informed lifestyle choices. Individuals suffering from this condition must take proactive steps to avoid activities that place unnecessary strain on the spine. Strenuous activities, typically characterized by high-impact exercises or heavy lifting, can exacerbate symptoms and lead to further complications. Thus, it is crucial for patients to engage in low-impact exercises that promote flexibility and strength without putting undue pressure on the vertebral discs.
In addition to opting for gentle physical activities, incorporating an anti-inflammatory diet can contribute significantly to alleviating pain and facilitating recovery. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and essential vitamins can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. A balanced diet not only supports overall health but also plays a vital role in managing herniated disks effectively.
Moreover, it is essential for individuals dealing with a herniated disk to seek comprehensive medical advice tailored to their specific condition. Healthcare professionals can provide insight into appropriate treatment options, including physical therapy and pain management strategies. Collaborating with specialists allows patients to develop a personalized management plan that aligns with their lifestyle and physical capabilities.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of lifestyle choices in managing herniated disks cannot be overstated. By avoiding strenuous activities, incorporating suitable exercises, and maintaining a healthy diet, individuals can effectively navigate their recovery journey. Taking these measures, along with professional guidance, can lead to improved function and a better quality of life for those affected by this challenging condition.



